Understanding Low Pressure Molding
Types of Low Pressure Molding
Importance of Device Durability
Methods in Low Pressure Molding
Latest Trends in Molding Technology
Strategies for Enhancing Durability
Future of Low Pressure Molding
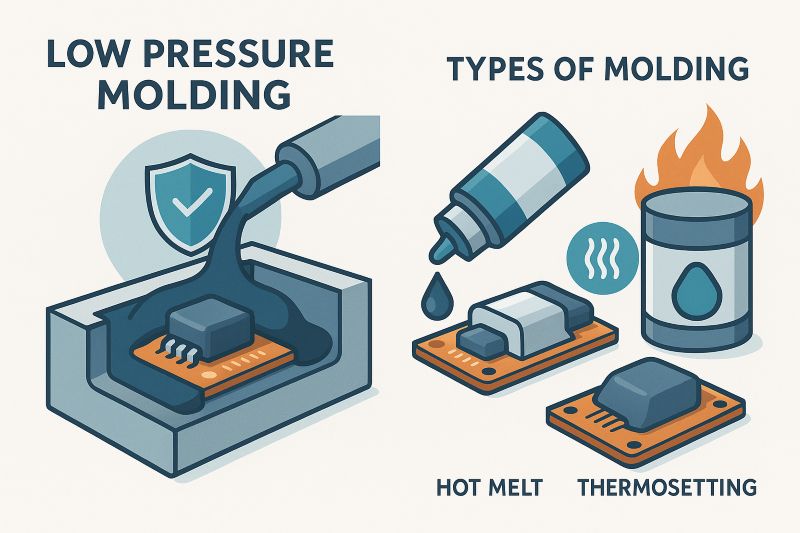
Low pressure molding (LPM) is an advanced process that encapsulates sensitive components using low-viscosity thermoplastics applied at gentle pressure. This technique minimizes mechanical stress, offering effective protection from dust, moisture, and vibration. Its low-temperature nature makes it ideal for delicate electronics, widely used in manufacturing environments requiring safe and efficient encapsulation.
There are primarily two common approaches to low pressure molding: hot-melt molding and thermosetting molding. Hot-melt techniques rely on fast-melting thermoplastics that offer strong adhesion and quick processing. Thermosetting options, in contrast, are known for high resistance to heat and chemicals after curing, making them suitable for demanding environments. Both methods ensure reliable protection tailored to application needs.
Modern electronics are increasingly expected to operate reliably in harsh environments. Low pressure molding plays a vital role in reinforcing device durability by shielding internal components from contaminants and mechanical damage. The encapsulation process not only improves product lifespan but also enhances user safety and performance consistency—critical factors in today's connected and mobile world.
Key molding techniques include overmolding and full encapsulation. Overmolding involves applying a secondary protective layer to exposed areas such as connectors or joints, while full encapsulation surrounds the entire component for maximum protection. These methods are adaptable to various product geometries and performance requirements, providing manufacturers with flexibility and reliability.
Recent developments in molding technology focus on sustainability, precision, and miniaturization. Thermoplastic materials with improved environmental resistance and lower ecological impact are gaining traction. At the same time, advancements in molding equipment now allow finer detailing and more compact molding operations—well-suited for next-generation devices requiring high functionality in small form factors.
To enhance device resilience through LPM, manufacturers should strategically select materials based on application-specific needs such as heat resistance, chemical exposure, or flexibility. Combining suitable materials with optimized process parameters—such as mold temperature, pressure control, and cycle time—ensures consistent results. Thorough training and process validation are also essential for quality assurance and long-term reliability.
The future of LPM is closely tied to trends in device innovation. As consumer and industrial electronics continue to shrink while demanding more robustness, the need for advanced molding methods will grow. Research into bio-based materials, automation, and digital process monitoring is expected to further elevate LPM’s role in ensuring functional, sustainable, and durable electronic systems.
What is low pressure molding (LPM)?
LPM is a process that encapsulates components with thermoplastic materials at low pressure and temperature, reducing stress and enhancing protection.
Which types of LPM techniques are most common?
Hot-melt and thermosetting molding are the most used. Hot-melt offers quick application, while thermosetting provides strong environmental resistance after curing.
How does LPM improve device durability?
LPM provides a physical barrier against dust, moisture, and mechanical shock, ensuring electronics maintain function over time.
What materials are used in LPM?
Various thermoplastics and engineered compounds are used depending on performance needs such as heat resistance, adhesion, or flexibility.
What are the latest developments in LPM?
Trends include miniaturization support, eco-friendly material development, and integration with precision molding technologies.
What strategies ensure better LPM results?
Key strategies include correct material selection, refined process controls, and attention to mold design and curing parameters.
Why is LPM relevant to modern electronics?
Its gentle application and strong protection make it suitable for delicate and compact electronics used in consumer, automotive, and industrial fields.
What is expected in the future for LPM?
Growth in smart devices, IoT, and wearable tech will drive innovation in LPM materials, automation, and high-efficiency encapsulation methods.