Definition of Hot Melt Adhesives
Types of Hot Melt Adhesives
Importance in Manufacturing
Application Methods
Latest Trends in Adhesives
Strategies for Implementation
Future of Manufacturing with Adhesives
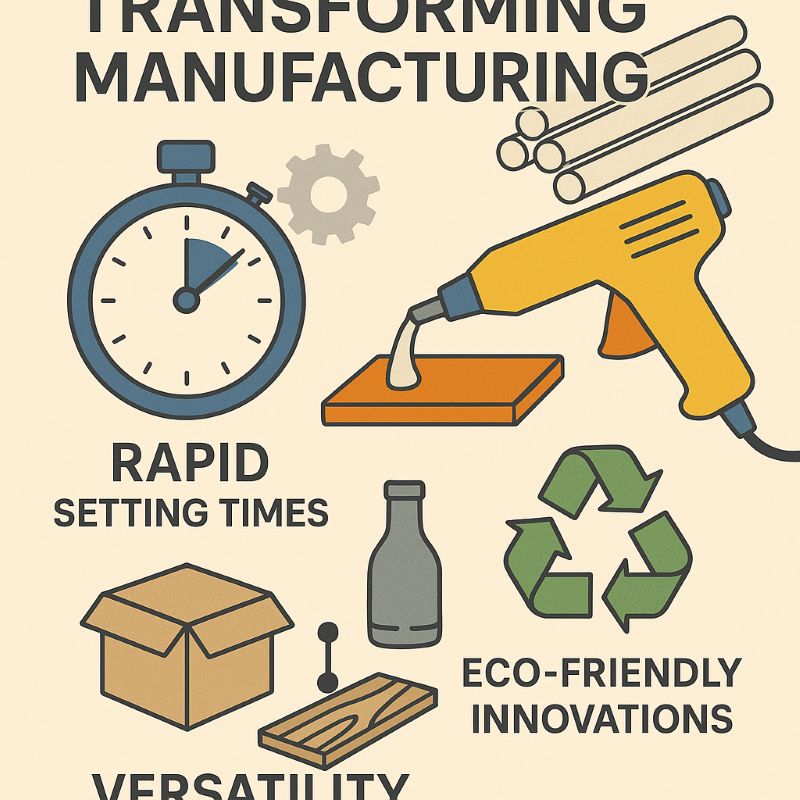
Hot melt adhesives are solid materials that melt when heated and form bonds as they cool. Their fast-setting properties and versatility make them increasingly valuable in modern manufacturing. These adhesives are compatible with various substrates and support efficient, environmentally conscious production.
In manufacturing, different types of hot melt adhesives serve specific needs. EVA-based adhesives are cost-effective and commonly used in general packaging and binding. Polyolefin adhesives offer resistance to chemicals and heat, making them suitable for electronics and automotive applications. Polyamide adhesives perform well in high-temperature environments, such as in textiles or industrial filtration. Pressure-sensitive hot melts maintain a tacky surface even after cooling, useful for applications requiring repositionability or long open times. Each type enhances performance based on application-specific demands.
Hot melt adhesives play a critical role in modern manufacturing by increasing production speed, enabling automation, and improving bond strength across substrates. Their ability to reduce downtime and energy use supports sustainable production. From packaging to electronics, these adhesives ensure product consistency and durability, helping manufacturers remain competitive while meeting environmental standards.
Common application methods for hot melt adhesives include roll coating, slot die coating, and spray application. Roll coating evenly covers wide surfaces. Slot die coating allows for precision, ideal for technical assemblies like electronics. Spray methods offer flexibility for irregular or complex surfaces. Selecting the right method based on adhesive characteristics and production needs improves efficiency, minimizes waste, and ensures strong bonding results.
Hot melt adhesives are evolving to meet the growing demand for performance and sustainability. Recent trends include eco-friendly formulations with low emissions, higher thermal resistance, and improved bonding strength. Manufacturers increasingly prioritize adhesives that reduce material waste and energy consumption, aligning with global environmental goals. These trends also enable broader adoption in sectors previously reliant on solvent-based or slower-curing adhesives.
To implement hot melt adhesive technologies effectively, manufacturers should assess process requirements and select adhesives based on thermal performance, bonding needs, and material compatibility. Application methods must align with product geometry and production speed. Partnering with adhesive suppliers for technical trials ensures optimal performance in real-world conditions. Training production staff on handling and equipment use also ensures consistent results and accelerates process improvements.
The future of hot melt adhesives lies in continuous innovation. Next-generation formulations are expected to offer better heat resistance, biodegradability, and compatibility with automation systems. As more industries seek sustainable and high-performance solutions, hot melt adhesives will become central to efficient, low-waste manufacturing. Their ability to meet complex bonding challenges will make them indispensable in packaging, electronics, textiles, and more.
What are hot melt adhesives?
They are solid adhesives that melt when heated and solidify to form a bond upon cooling. Known for quick setting and broad material compatibility.
What types of hot melt adhesives exist?
The main types include EVA, polyolefin, polyamide, and pressure-sensitive adhesives. Each serves unique purposes depending on temperature, flexibility, and surface compatibility.
Why are hot melt adhesives important in manufacturing?
They improve production speed, bond strength, and sustainability by reducing waste and energy consumption.
How are hot melt adhesives applied?
Common methods include roll coating, slot die coating, and spray application, each suited for different surface types and production needs.
What trends are influencing hot melt adhesive use?
Sustainability, VOC reduction, thermal stability, and automation compatibility are key drivers of innovation in this field.
How can manufacturers adopt hot melt technologies?
Start with needs assessment, adhesive selection, trial applications, and employee training to ensure smooth integration.
What’s the future of adhesives in manufacturing?
Expect smarter, greener adhesives that support higher productivity and lower environmental impact across industries.
Are there notable product examples?
This guide focuses on general categories. Manufacturers should consult suppliers for suitable formulations based on their industry and application.